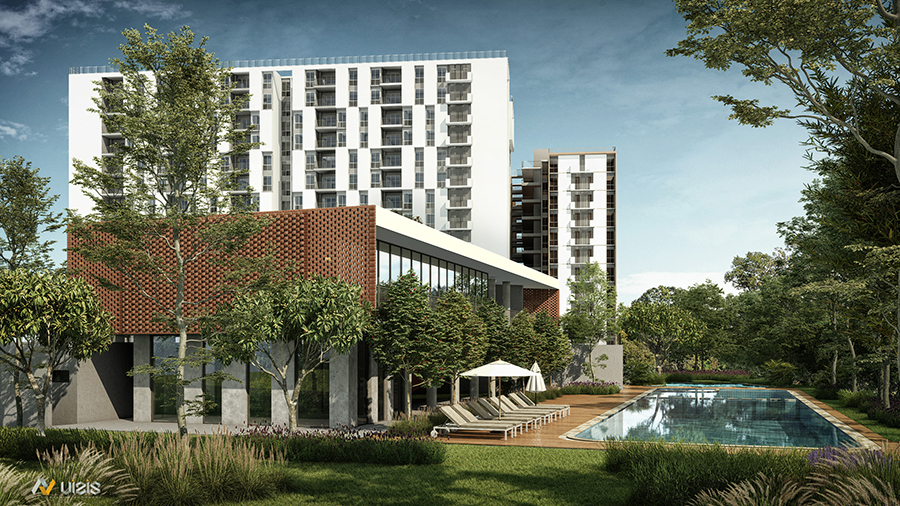
Places Worth Living For

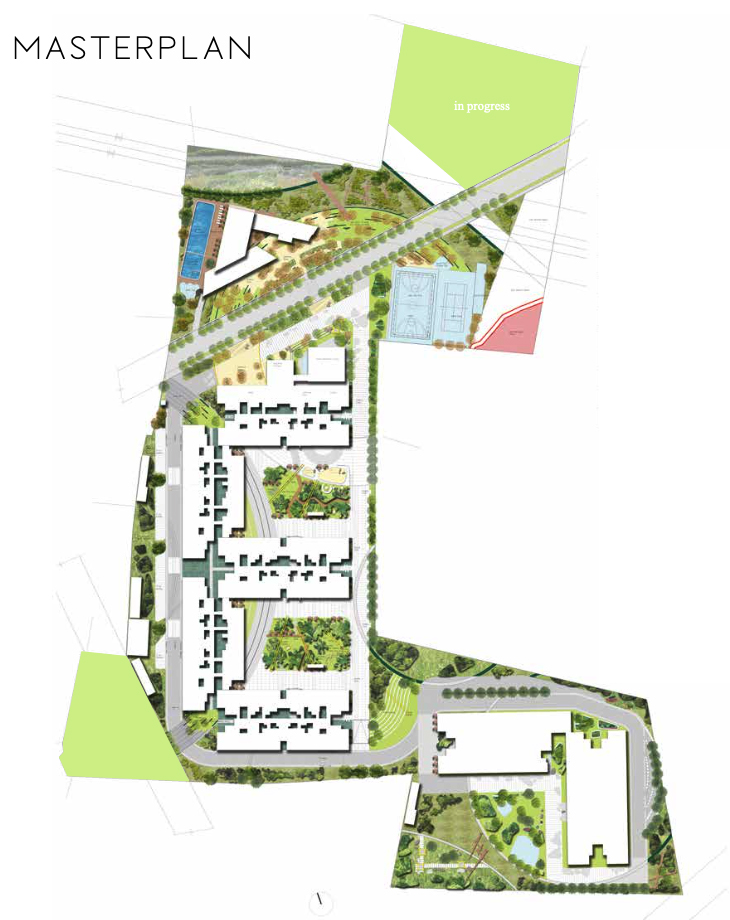
Program: Residential
Area: 15.5 Acres
Client: Assetz Property Group
Status: Schematic
Location: Bangalore, South India
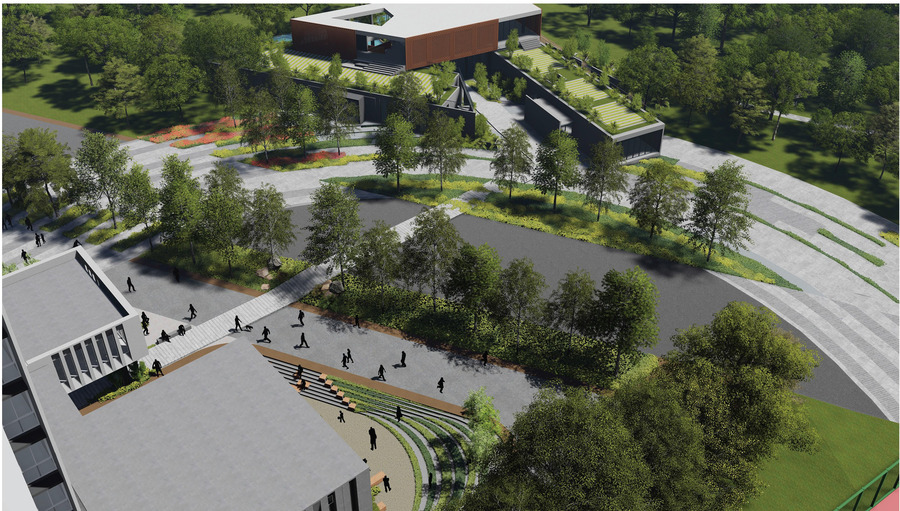
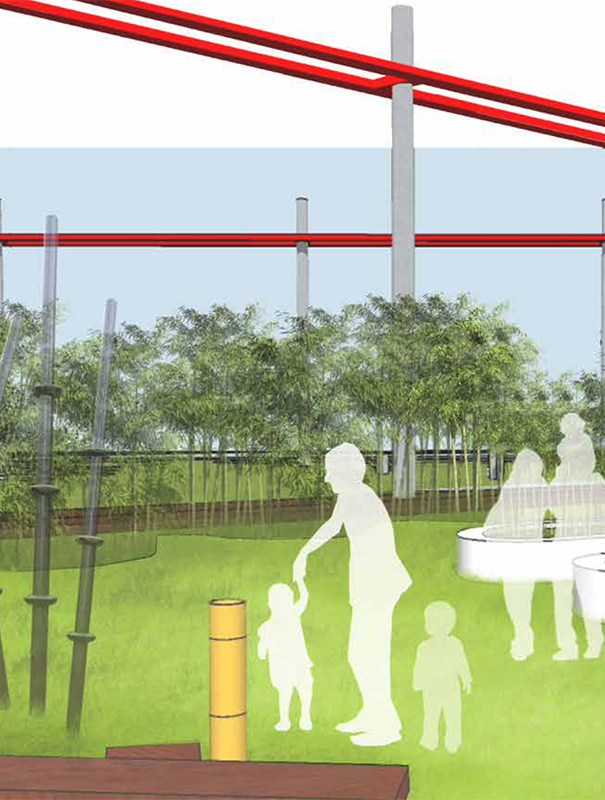
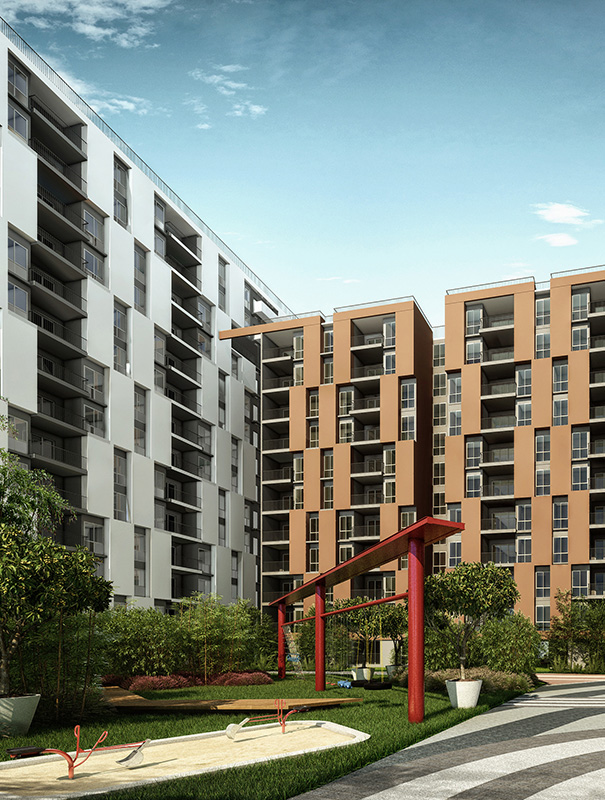
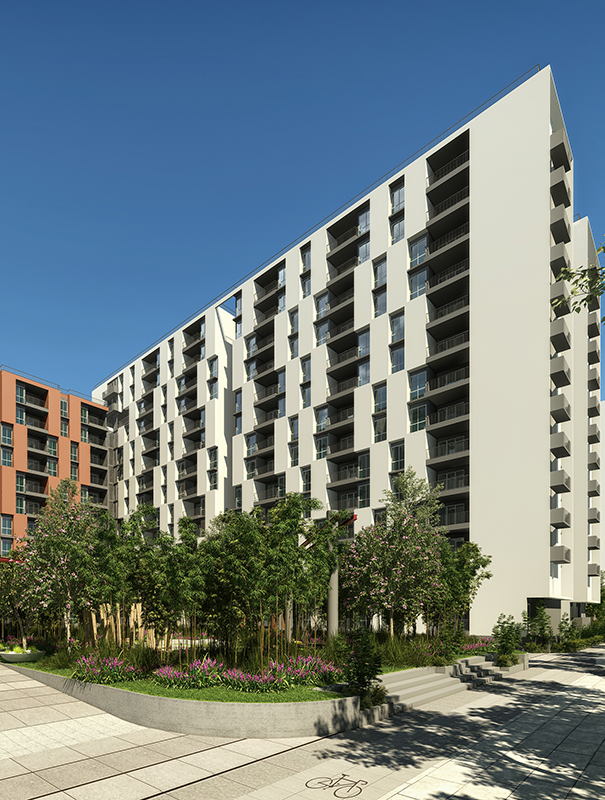
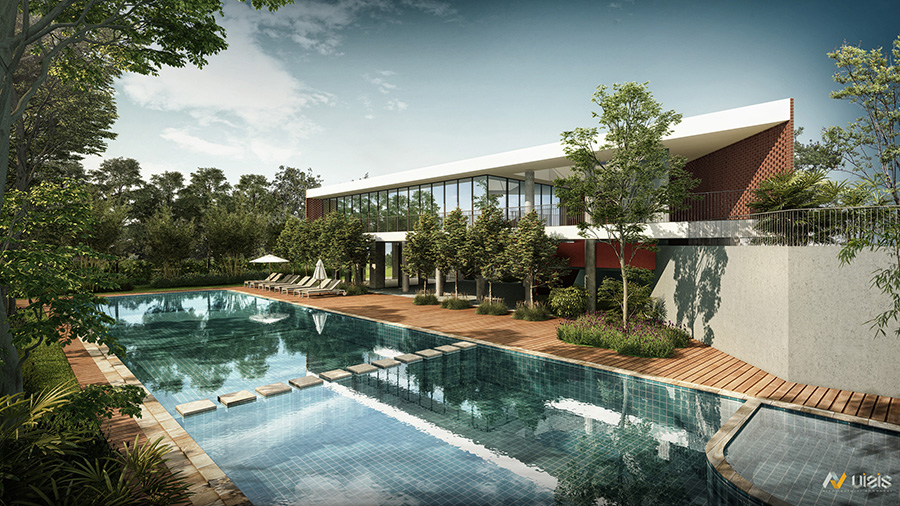
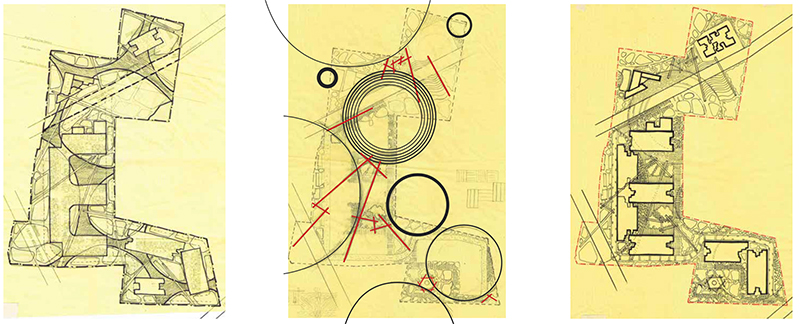
The landscape design of Shettigere is the result of an amalgamation of the Indian cultural and geological context of the site with the Japanese Garden design philosophy. The design is evolved in three layers with the context layer forming the first layer leading the organization of the landscape space, the second layer adding the human scale to it, and finally, the third layer adding interest and functionality to the external space through vertical elements.
CONTEXT LAYER – THE ORGANISATION OF THE SPACE
A. The quarries surrounding the site boundary enhance the profile of the area. The most common purpose of the quarry is to extract various stones for building materials from the surface of the earth. Different types of stones are mined for different purposes and are extracted in different shapes. This leads to a design pattern that depicts the different shapes of the granites extracted.
B. According to Ancient Japanese mythology, the mountains and stones create the skeleton of the Earth and symbolize permanence and immutability, the water is its blood, a symbol of the flow of life and change. Therefore, stones form the frame of a Japanese garden. If they are properly arranged, the other part of the garden should automatically arrange itself. The art of the stone arrangement Sute- ishi (japanese: sute-ji – “build” + ishi-”stone”) at all times was considered the main element in the gardener’s work
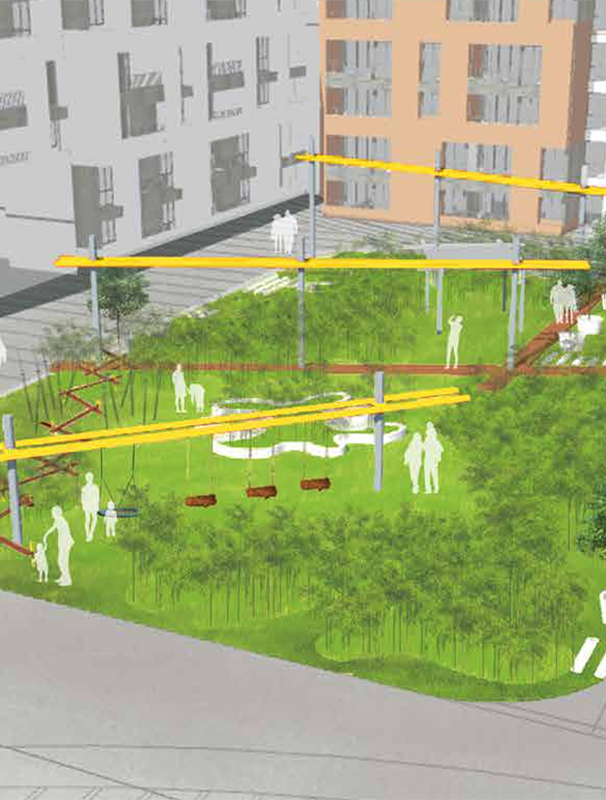
HUMAN SCALE – THE CIRCLE IN ITS MANY MEANINGS
A. Muthiyalamma temple, situated in the precinct of the site is famous for the rituals performed to the Goddess through the colorful bangles. The bangles play a significant role in the Hindu culture and are one of the important ornaments worn by women. The circle represents eternity, timelesness, and also the cyclic movement of life.
B. In Japanese culture, the circle symbolizes enlightenment, the gourd happiness. The circles are connected to nature which indicates the rippling of water.
BINDING ELEMENTS – THE VERTICAL ELEMENTS
A. The term “granitic” means granite-like and is applied to granite and a group of intrusive igneous rocks with similar textures and slight variations in composition and origin. Due to the natural conditions of the rocks, some granites may have linear textures. This unique pattern lead lends its form to the landscape design.
B. The straight lines leading to verticality is a significant symbol of Japanese Architecture, which is traditionally been typified by the wooden structures elevated slightly elevated from the ground
CONTEXT LAYER – THE ORGANISATION OF THE SPACE
A. The quarries surrounding the site boundary enhance the profile of the area. The most common purpose of the quarry is to extract various stones for building materials from the surface of the earth. Different types of stones are mined for different purposes and are extracted in different shapes. This leads to a design pattern that depicts the different shapes of the granites extracted.
B. According to Ancient Japanese mythology, the mountains and stones create the skeleton of the Earth and symbolize permanence and immutability, the water is its blood, a symbol of the flow of life and change. Therefore, stones form the frame of a Japanese garden. If they are properly arranged, the other part of the garden should automatically arrange itself. The art of the stone arrangement Sute- ishi (japanese: sute-ji – “build” + ishi-”stone”) at all times was considered the main element in the gardener’s work
HUMAN SCALE – THE CIRCLE IN ITS MANY MEANINGS
A. Muthiyalamma temple, situated in the precinct of the site is famous for the rituals performed to the Goddess through the colorful bangles. The bangles play a significant role in the Hindu culture and are one of the important ornaments worn by women. The circle represents eternity, timelesness, and also the cyclic movement of life.
B. In Japanese culture, the circle symbolizes enlightenment, the gourd happiness. The circles are connected to nature which indicates the rippling of water.
BINDING ELEMENTS – THE VERTICAL ELEMENTS
A. The term “granitic” means granite-like and is applied to granite and a group of intrusive igneous rocks with similar textures and slight variations in composition and origin. Due to the natural conditions of the rocks, some granites may have linear textures. This unique pattern lead lends its form to the landscape design.
B. The straight lines leading to verticality is a significant symbol of Japanese Architecture, which is traditionally been typified by the wooden structures elevated slightly elevated from the ground